Maintaining State
Learning Goals
- Understand how cookies impact our experience on the internet
- Implement a simple cookie
- Recognize some limitations and regulations with cookies
Warm Up
With a Partner
Based on your experience interacting with websites:
- What is a cookie?
- How do you know if a website uses cookies?
If you Give a Dev a Cookie
HTTP is a stateless protocol. This means that each request to a server exists in isolation - the server makes no connection between one request and the next. This makes for a very boring internet! If we stayed in a stateless environment, we wouldn’t be able to log in to applications, or save personal preferences, and the online shopping experience would be much more difficult.
Independent Research Spend 20 minutes researching cookies in web development. Try to answer the following questions:
- In technical terms, what is a cookie?
- Where are cookies stored?
- How do you create a cookie in a .NET web application?
Be ready to share out!
After giving students time to research, lead a discussion to answer these questions. Make sure to hear from all voices in the room! We want students to understand:
- Cookies are small pieces of data that are passed to servers from the client
- Cookies are stored on instances of a client (this chrome browser, or this google user)
- Cookies are typically created by a server
- Cookies can be created by a client, but not all servers will accept them or do anything with that info (dark mode).
Inspecting Cookies
Are you ever curious about what cookies are following you around? With chrome dev tools, you can see the cookies that exist for a website that you are on!
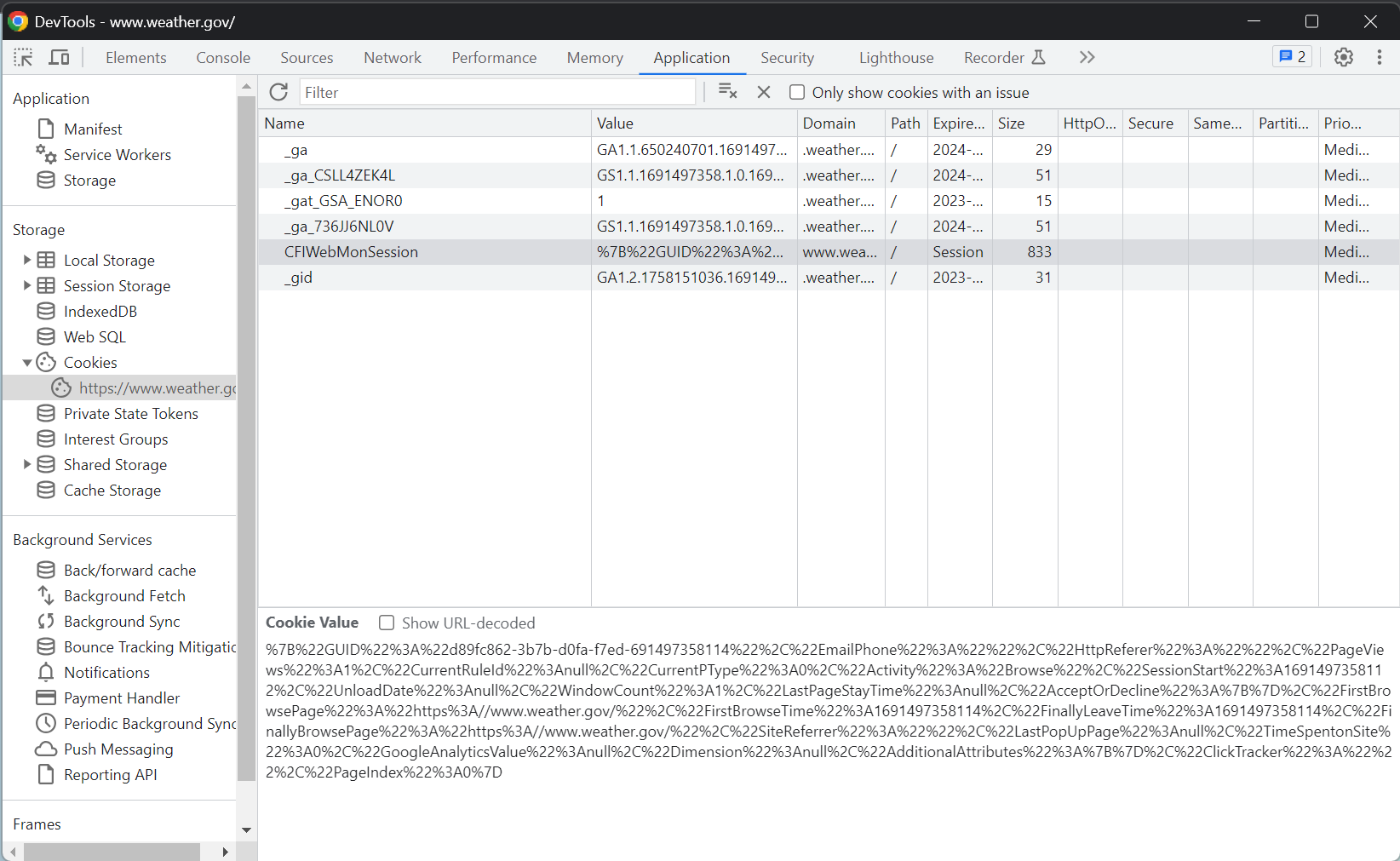
Try It! In your browser, check out the cookies at some of your favorite websites. How do these cookies change if you visit these sites in ‘incognito’ mode?
Cookies in .NET
To create a cookie in .NET we can add key/value pairs to the Response object. All cookies are made of a key/value pair where the key and value are both strings (everything on the internet is strings!).
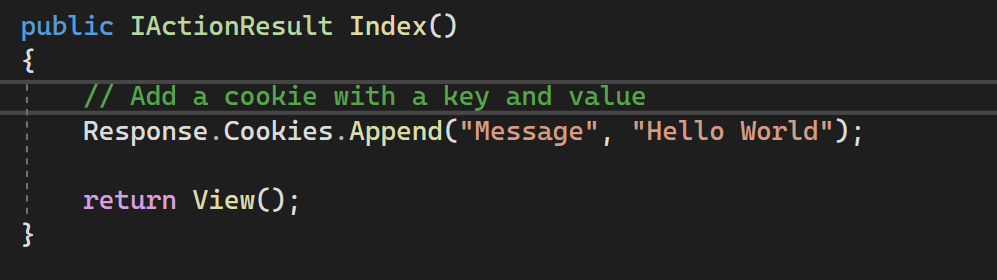
This cookie will be set everytime a request is made:
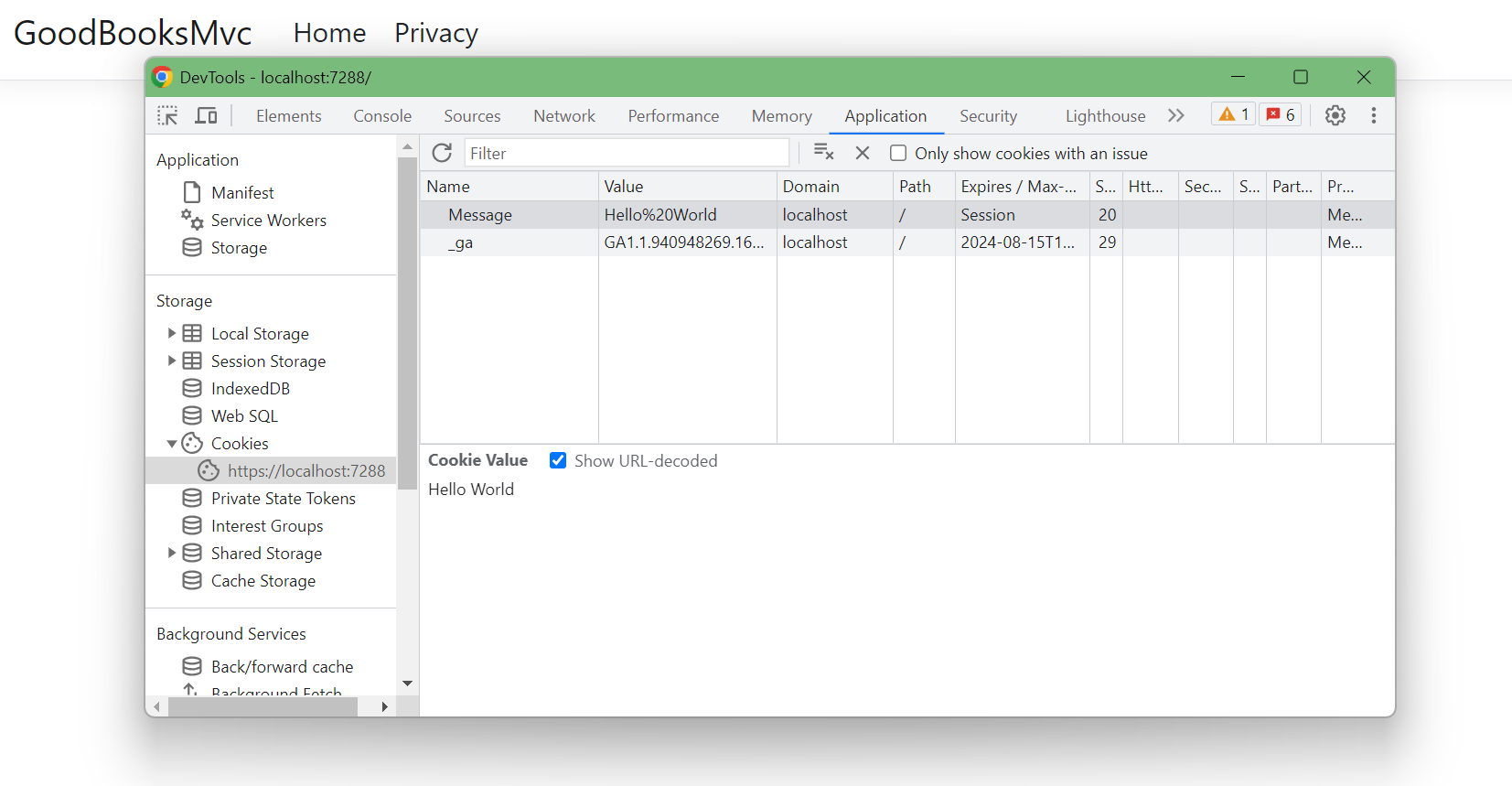
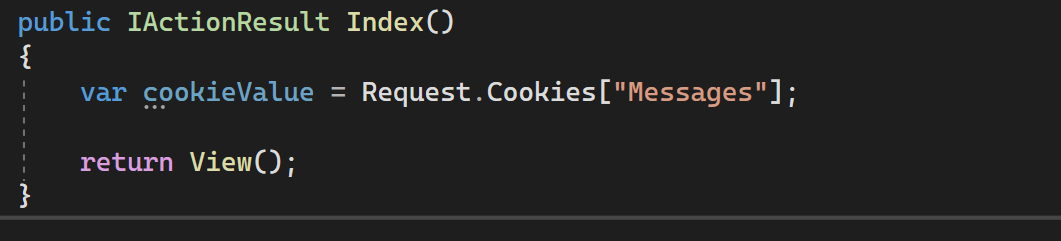
We can read cookies by asking or the values at specific keys from our Request object.
The following activity could be completed individually, in groups, or a mix (start individually then switch to groups or vice-versa). Ask students to share their solutions at the end. Here is a possible solution:
public IActionResult Index()
{
var visitCount = Request.Cookies["visitCount"];
if (visitCount is null)
{
Response.Cookies.Append("visitCount", "1");
ViewData["visitCount"] = 1;
}
else
{
visitCount = (Convert.ToInt16(visitCount) + 1).ToString();
Response.Cookies.Append("visitCount", visitCount);
ViewData["visitCount"] = visitCount;
}
return View();
}
Implement a Cookie
Let’s try it out. Fork and clone this starter repo
Using cookies, implement the following user-story:
As a User
When I visit the home page ('/')
Then I see a count of how many times I have visited the page
Each time I refresh, I see that the count increases by 1
Be ready to share your solutions!
As students are sharing out, discuss how cookies are being sent in requests - all cookies associated with that domain will be passed back and forth - the view doesn’t matter.
Regulations
Because cookies are used to track user data, we have seen a lot of security and privacy issues discussed. There have also been legal regulations set out in certain states and countries to govern how this data can be used. For more info on this, take a look at cookielawinfo.com
Checks for Understanding
- Why are cookies necessary for modern web-development?
- What are some drawbacks to using cookies?